May 16, 2025
What You Should Know about Low Voltage Cable
Getting to Know Low Voltage Cable
What Is Low Voltage Cable?
Low voltage cables are electrical components that work at 3,000 volts or less. They’re super important for transmitting power safely and smoothly in all kinds of places. These cables are built to handle low-power jobs while keeping things safe and reliable. What’s cool about them is how they fit into so many settings, like underground systems, factories, or even your home. For example, low voltage lighting systems often use these cables because they’re trustworthy and efficient.Some types of these cables come with extra protection to stand up to rough conditions. Take the NAYY (VLV) cables—they’re made for delivering power in low voltage setups. They’re great for underground use in industrial spots with added shielding. Then there are the NA2XBY (YJLV22) cables, which can take some physical stress but aren’t meant for heavy tugging.
Where You’ll Find Low Voltage Cables
These cables are incredibly versatile, popping up in all sorts of industries. One big use is in low voltage lighting, where they connect light fixtures to power sources without a hitch. You’ll also see them in home wiring, hooking up industrial machines, or setting up networks in office buildings.Cables like the NA2XRY (YJLV32) are perfect for indoor spots, tunnels, trenches, shafts, or even buried underground. That makes them a go-to for things like transformer stations or power plants. Plus, waterproof connectors for these cables keep things reliable in wet or outdoor areas.
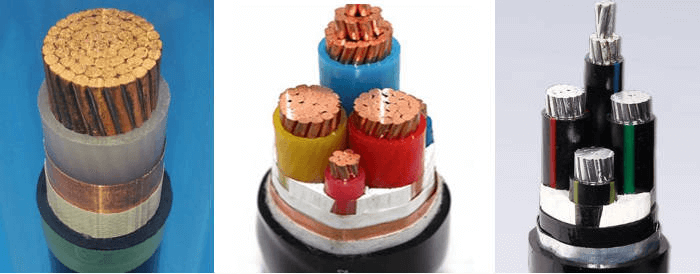
Types of Low Voltage Cables
Shielded vs. Unshielded
Shielded cables have an extra layer to block out electromagnetic interference (EMI). This is handy in places with lots of electrical noise or sensitive equipment. Unshielded cables, on the other hand, skip this layer. They’re more flexible and cheaper, great for simple setups.A technician might pick shielded cables for tricky systems that need clear signals. But for basic home projects, an installer might go with unshielded ones.
Single-Core vs. Multi-Core
Single-core cables have just one conductor wrapped in insulation. They’re used for straightforward power jobs. Multi-core cables pack several conductors into one sheath, perfect for more complex tasks with multiple connections.For example, N2XY (YJV) 0.6-1kV cables are multi-core and can be set up on trays or in conduits. They’re awesome for low voltage systems where you need several circuits running at once.
Insulation Materials
The stuff used to insulate these cables really matters for how well they work and how long they last. Here are the main ones:- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): Cheap and bendy.
- XLPE (Cross-Linked Polyethylene): Stands up to heat and lasts a long time.
- Rubber: Super stretchy and tough against wear.
to stay durable. XLPE insulation has to pass heat-extension tests before it’s good to go.
These materials decide how well a cable holds up in different environments. A connector for these cables needs to match the insulation to keep connections solid.
Low voltage cables keep getting better with new tech and materials. Whether you’re installing cables, working as a technician, or setting up networks, knowing this stuff helps you get the job done right.
What to Think About When Choosing Cables
Power Performance
When you’re picking out low voltage cables, you’ve got to think about how well they carry power. This affects how efficiently they work. Materials like copper or aluminum are often used because they conduct electricity so well.Take N2XY (YJV) 0.6-1kV cables—they’re designed for low voltage power systems. You can mount them on trays, in conduits, or even on walls. Choosing the right cables means less energy waste, which is key for things like lighting or structured cabling.
Durability and Toughness
Handling Heat, Water, and ChemicalsDurability is a big deal for low voltage network cables. They need to stand up to heat, moisture, and chemicals without falling apart. Sheath like PVC or HDPE helps with this.
For example, NA2XRY (YJLV32) cables are great for indoor use, tunnels, trenches, or buried setups. They’re tough enough to handle physical stress and environmental challenges, making them ideal for power plants or transformer stations.
In wet outdoor spots, waterproof connectors keep water out, preventing short circuits or rust.
Lasting Through Tough Conditions
A cable installer’s work stays solid if the cables can handle different environments. Whether they’re underground, in changing temperatures, or under stress, they need to keep working.
Cables like NAYBY (VLV22) are made for underground industrial use with extra protection. They can take some physical force but aren’t built for heavy pulling. Picking the right cables keeps systems running in tough spots.
Following Industry Rules
You can’t skip industry standards when choosing cables. These rules ensure the cables are safe and work as expected. They also make sure cables work with things like connectors and fixtures.
For example, aluminum alloy conductors are annealed to improve their flexibility, creep resistance and corrosion resistance, and their comprehensive performance has reached the international advanced level. Even if the cable is overloaded and heated for a long time, the stability of the connection can be guaranteed.
Using cables that meet these standards gives technicians confidence that their systems are safe and reliable.
TDDL’s Top-Notch Low Voltage Cables
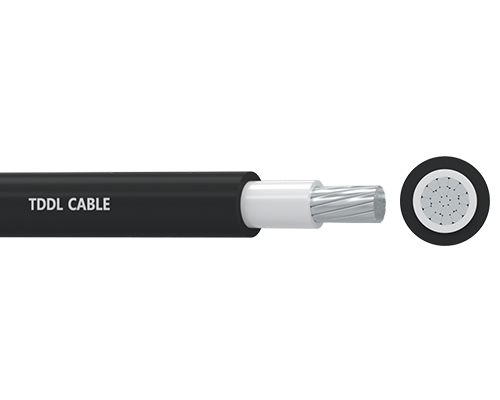

TDDL offers a wide range of high-quality low voltage cables for all kinds of jobs. Our products are made with cutting-edge materials and processes for great performance and long life.
For example, TDDL’s NA2XY (YJLV) 0.6-1kV cables are perfect for underground industrial use with added protection. You can set them up on trays or in conduits, making them super versatile.
TDDL also has cables for specific needs. Our N2XRY (YJV32) 0.6-1kV cables work indoors, in tunnels, or buried setups. They are strong enough for external forces and tough setups like power plants or transformer stations.
Installers and technicians working on structured cabling love TDDL’s products. We meet strict standards and work in all sorts of scenarios. Whether it’s home wiring or big industrial networks, TDDL has you covered.
Looking for cables for lighting systems or waterproof connectors? TDDL’s got reliable options. Our focus on quality makes them a go-to for all your low voltage cable needs.


